Shoulder Surfing
- Reading time:
- 10 min

Do you always know who is looking over your shoulder? When you’re working on your tablet on the train, it can easily happen that someone is looking at your screen without you noticing.
Shoulder Surfing
In our blog, we regularly inform you about technical possibilities such as phishing, adware or worms that are used to obtain personal data such as login details. However, there are also completely non-technical ways to obtain such data, above all so-called shoulder surfing. In this blog post, we want to shed some light on this possibility of illegal data theft.
What is shoulder surfing?
Shoulder surfing is a technically simple and uncomplicated way to read out personal data. In shoulder surfing, a person observes their victim interacting with devices such as a laptop, cell phone or bank terminal and attempts to access sensitive data. In principle, this can involve all types of data, such as business data, bank data or login data.
As is customary in the IT security context, we will simply refer to the person observing the attack as the attacker in this article.
Where does the term shoulder surfing come from?
Figuratively speaking, the shoulder surfer looks over the shoulder of the victim when interacting with the respective end device. Where exactly the term shoulder surfing comes from, however, is actually somewhat unclear. In connection with the water sport of the same name, it is sometimes referred to as shoulder surfing, meaning surfing on a wave that is already being ridden by another surfer. One assumption is that the analogy shoulder surfing initially referred to reading along while surfing the web, i.e., surfing on the same “information wave” as the active user, and that it was only later recognized that shoulder surfing is a security risk. But as I said, this is admittedly a guess. The exact origins of the term do not appear to be entirely clear. Regardless, the term seems metaphorically apt.
How does shoulder surfing work?
In shoulder surfing, the attacker observes his victim interacting with a device and attempts to read out sensitive data. This is often done knowingly and with criminal intent.
The fact that shoulder surfing is possible at all is due to our sometimes overly careless handling of sensitive information. We are all familiar with the situation where we are sitting in a café or on the train and want to quickly read up on something for work. We have quickly opened an Excel spreadsheet with the quarterly accounts or personnel data, without making sure who might be sitting behind us. The well-placed person sitting next to you or the curious passenger on the train may also think that the information you have called up could also be of interest to outsiders and eagerly read along.
Shoulder surfing and its relatives
As with any other type of attack, there are also different ways of attacking with shoulder surfing. We have described the classic type of attack above: Someone seizes a favorable opportunity and watches someone else interact directly with a terminal device. However, there are also variants of shoulder surfing that do not follow the standard pattern. In the following, we would therefore like to take a look at some related phenomena of shoulder surfing.
In times of increased video calls and constant selfies, looking over the victim’s shoulder from the side of the camera, for example, can also lead to interesting insights.
Reversed Shoulder Surfing
Admittedly, the term reversed shoulder surfing does not yet exist, but it could certainly refer to a new but very related type of shoulder surfing. Consider the following situation: you look through the camera of a PC at the background, in the sense of a user’s room behind it, for example during a video call. The equipment that is then visible can also provide interesting information, especially if the background shows a whiteboard on which strategy plans or similar are sometimes sketched. To avoid such situations, many companies have corresponding whiteboard policies that determine what may be displayed on the whiteboards for longer periods of time.
The arrest of a suspected criminal influencer at the end of 2022 led to some speculation in this context. The influencer in question was seen in a Twitter video with some pizza boxes from a particular brand in Bucharest - he was arrested shortly afterwards. This led to speculation as to whether the pizza boxes may have provided clues as to his whereabouts.
Whether the pizza boxes actually had anything to do with the arrest has unfortunately not been clarified (WDR), but the story shows that you should definitely pay closer attention to where you point the camera - and not just when you’re being wanted by the police.
Unintentional shoulder surfing?
Shoulder surfing generally refers to the deliberate spying on personal data with criminal intent. In principle, however, there is certainly the possibility of unintentional shoulder surfing. This situation is also easy to imagine: You walk into the office and look directly at the screen of a colleague who just had to go around the corner but forgot to lock their screen. You then have full access to their documents or their personal chat with the boss. Strictly speaking, such a situation is also a form of data leak, but the hope remains that the consequences will be less serious (which in this case probably depends more on the working atmosphere) than a shoulder surfing incident with criminal intent.
Shoulder surfing and social engineering
In the security context, social engineering refers to the targeted influencing of people in order to induce certain behaviors, e.g., so that the victim discloses confidential information. One technical way of social engineering is phishing, for example: the victim is tricked into clicking on a certain link in an email. Less technical is the famous grandparents scam, in which a criminal calls elderly people and pretends to be a grandchild or other relative in order to obtain financial benefits. Another social engineering technique is to examine the victim’s garbage. This may sound a bit hare-brained at first, but if you think about it, our garbage reveals a lot about our personal interests and preferences. Shoulder surfing can be used as a social engineering technique. A quick glance at the open tabs in the victim’s browser also reveals a great deal about their preferences and interests. This enables the attacker to create a coherent picture of their victim in order to quickly interact with them on a supposedly trusting level and obtain sensitive data.
The personal handling of data
Shoulder surfing with criminal intent is of course a security problem and even with great care, the risk of falling victim to such an attack cannot be completely eliminated. Even if you are alone in the office, you do not know on which building roof someone is hiding and looking at the monitor with binoculars. Such a scenario is more reminiscent of an agent thriller than our everyday experiences, but depending on the relevance of the stolen data, it is not so far-fetched. In this context, it has recently come to light in the media, for example, that some members of the German parliament had their offices directly opposite the Russian embassy. As an anti-espionage measure, these members of parliament were advised to at least keep the blinds permanently closed.
In most cases, however, we are not so careful with our data that binoculars or secret cameras are necessary. The phenomenon of the businessman who tells a packed train which customers he is currently visiting and what he is presenting there has not yet died out. An acquaintance once told me the following anecdote in this context: For a while, she took the train to work every morning, and every morning at the same time, a stranger spoke loudly on the phone, talking about house-building projects, plans for children (her own and those of friends), grandma’s illness, etc. One morning, my friend got fed up with this, sat down next to the person on the phone and asked her about her grandmother’s health, the children and the new house. The person was probably a bit resigned and responded with a remorseful “I understand”. In view of such careless behavior, it’s no wonder that shoulder surfing and social engineering sometimes work so well.
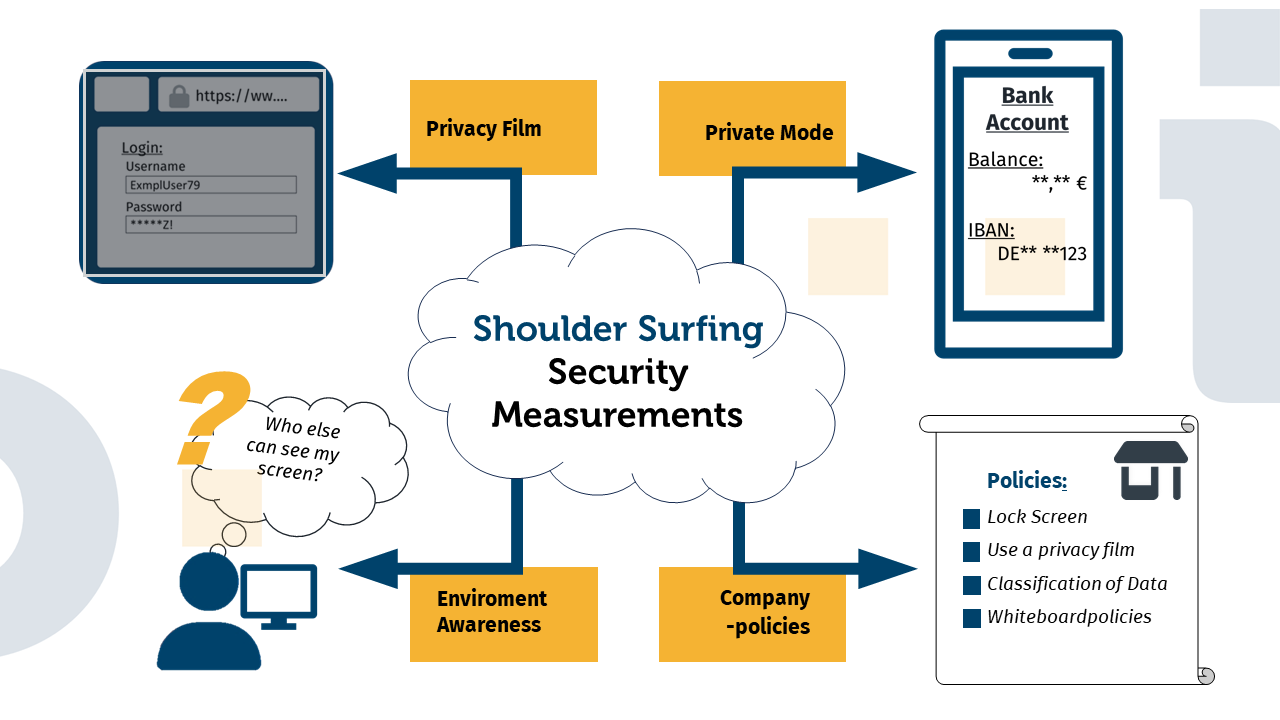
Preventive measures against shoulder surfing
Shoulder surfing has now been recognized as a safety problem. Accordingly, there are now a number of technical ways to protect yourself against shoulder surfing. We will discuss some of these safety measures below.
Privacy screens and privacy shields
A very widespread and fairly simple technical precautionary measure are privacy shields, such as those used over the payment entry pad at ATMs, which have thankfully replaced the hand-over-numbers technique. Another technical solution is privacy films for laptops, tablets and smartphones, which can be easily applied to the screens. These films prevent a stranger from looking at the screen from the side without being asked and reading what is on it.
Private mode on apps
Some apps, especially banking apps, now also offer special private modes that are explicitly designed for using the app in public spaces. In private mode, sensitive content is not displayed at all or is only hidden by a special icon.
Safe handling of data
Regardless of technical solutions, personal behavior is, of course, still important. It is therefore advisable to be aware of your immediate surroundings from time to time: Who could be inspecting me from where, where is my screen turned to, is there a way to quickly get some space if in doubt or to end the interaction currently in progress on the end device, etc.? It is also advisable - especially in the office - to lock your screen or even the entire end device when you leave your desk. Even if you are only working with seemingly harmless content, you never know what might be of interest to external parties.
Company policies
Some companies have specific privacy policies that define which data may be viewed in which environment. Data is often classified according to a traffic light system (e.g., public data, internal data, confidential data, etc.), with explicit instructions to employees not to view confidential data in the public area. Corresponding whiteboard guidelines to prevent shoulder surfing through video calls have already been mentioned above.
Protective measures against shoulder surfing
Privacy screens and privacy shields: Privacy screens and privacy films offer an easy way to prevent unwanted glances.
Privacte mode on apps** Some apps offer options for making sensitive data unrecognizable in public spaces.
Safe handling of data** The conscious handling of personal data already prevents many cases of shoulder surfing.
Company policies** Many companies define privacy policies that specify the criticality of documents in order to prevent very sensitive data from being displayed in the public domain at all.
Conclusion
Shoulder surfing is a technique in which an attacker closely observes their victim interacting with a digital device in order to gain insight into their personal data. In this way, the attacker can succeed in accessing the victim’s passwords, PINs and other personal data. Shoulder surfing can also be used as a social engineering technique. In this case, the collected data is used to gain the victim’s trust, for example. As with all attacks, there is no one hundred percent protection against shoulder surfing, but with simple means such as privacy screens, careful handling of personal data, and occasional observation of your surroundings, you can protect yourself quite well from prying eyes.
Here you can gain even more insight into some of the issues addressed:
If you have any further questions about data security, account security or Identeco’s services, please contact us by email or make an appointment with us here!


Artikel teilen