The Banshee Information Stealer: The New Threat for Macs
- Reading time:
- 7 min
- What is Stealerware?
- What is the Banshee Stealer?
- Protecting Against Account Compromise Through Leaked Credentials
- Conclusion
What is Stealerware?
Banshee falls into the category of stealerware – a specific type of malware characterized by its stealthy and targeted data theft. But what exactly differentiates stealerware from other types of malware, and why does it pose such a significant threat?
Stealerware (or information stealers) refers to a class of malware designed to extract specific data from an infected device and transmit it to the malware’s creators. Unlike many types of ransomware, which become noticeable at a certain point (typically during or after encryption), stealerware operates most effectively when it runs unnoticed in the background. Especially if the infected system remains compromised for a long time, large amounts of data can be collected.
Stealerware typically goes undetected while continuously gathering sensitive data. This includes hardware information, screenshots, IP addresses, cookies, and other personal data. Particularly dangerous is its access to password managers, where highly sensitive data such as service URLs, usernames, and passwords are stolen. These data can be directly used for unauthorized access to accounts, which can have severe consequences for the affected individuals.
The high-quality data extracted by stealerware are transmitted in the background to the attacker. The stolen data can be easily used to log into accounts and gain access to data, funds, or other systems. However, the attacker often does not use the data themselves to log into accounts or launch other attacks. Instead, stolen data are typically sold or traded on online marketplaces in the dark web. Due to the data’s freshness and quality, they command a high value there.
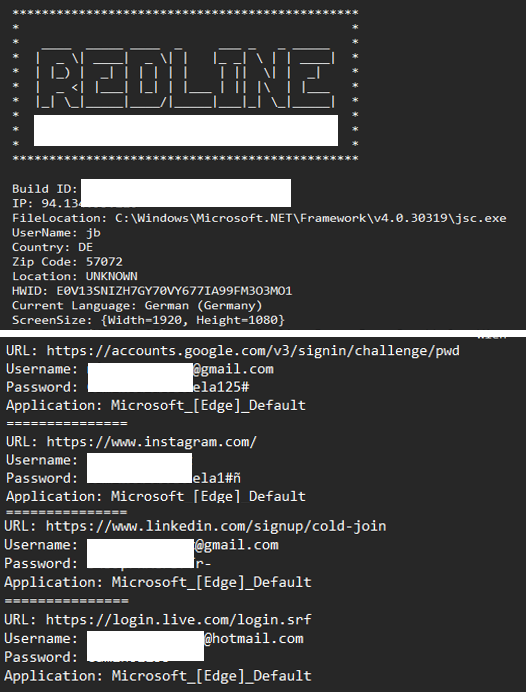
A particularly well-known example of stealerware was the so-called RedLine, first observed in 2020. The image above shows a screenshot of a data collection compiled by RedLine - a so-called stealer log - and gives a good impression of the data quality extracted by RedLine.
What is the Banshee Stealer?
The Banshee Stealer is a new type of stealerware specifically designed to infect Apple products, particularly Macs. It was first reported on August 15th by researchers at Elastic Security Lab and was named accordingly.
What Does the Banshee Stealer Collect?
Banshee collects a variety of system information, including hardware and installed software details. It also has access to the Notes app database, some file formats on the desktop and in the “Documents” folder, as well as Safari cookies. In other browsers – such as Firefox, Chrome, and Brave – Banshee grabs not only cookies but also browsing history, logins, and data from around 100 browser extensions. Banshee also shows particular interest in crypto wallets, highlighting the growing danger for users of digital currencies. The loss of access data to wallets can have serious financial consequences.
Why Cookies?
A specific type of cookie, the session cookie, remembers when a user had an authenticated session with a provider. These cookies typically have a limited expiration time. However, within this time frame, simply loading a stolen session cookie into the browser can take over an active session with the provider. Even if two-factor authentication is enabled with the provider, a session can often be taken over using a session cookie. This makes cookies in the wrong hands a very dangerous tool for taking over accounts.
Where Does the Banshee Stealer Come From?
It is suspected that the Banshee Stealer originates from Russia, based on the fact that the infection aborts when the system language is set to Russian. This approach is commonly seen in malware from certain regions to spare local users. However, this remains a speculative assumption.
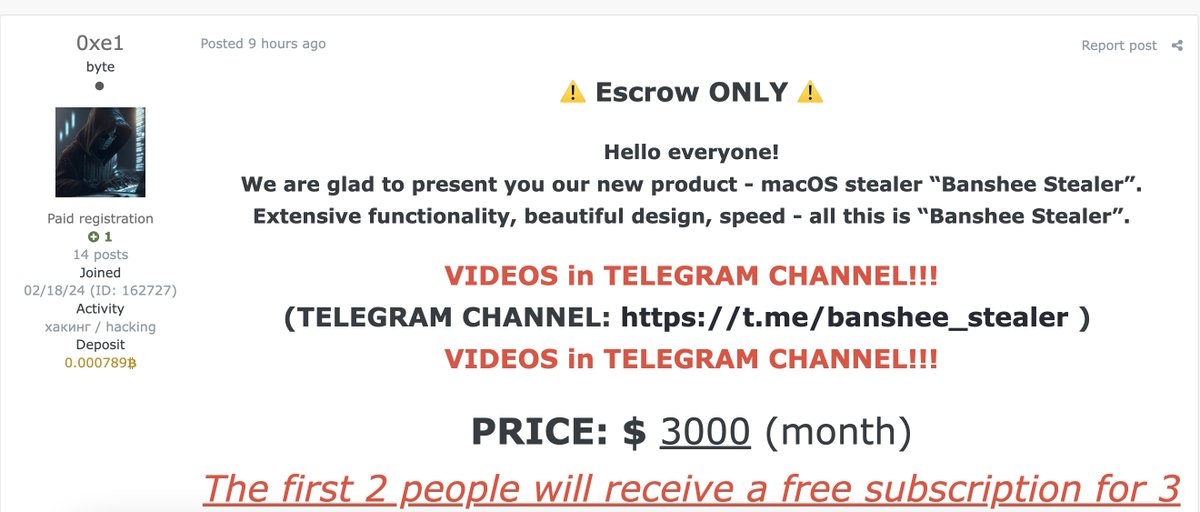
According to a screenshot shared on X/Twitter, a monthly license for the Banshee Stealer costs $3,000. This price is on the higher end for stealerware, suggesting a growing demand for specialized malware targeting Apple products. The high price may indicate Banshee’s effectiveness and specialization, which increases the potential risks for users.
How Does Banshee Work?
Banshee extensively uses the shell command ‘osascript’, a tool typically executed via the command line to run AppleScripts and JavaScript. This legitimate function is exploited by Banshee to gain extensive access rights after obtaining the system password – this includes the freedom to read sensitive data. This means that Banshee does not exploit known security vulnerabilities in an Apple system; instead, it relies on user authorization.
Users should therefore be mindful of when and where they enter their system password, particularly in response to unexpected or unusual requests.
Who Is at Risk?
Banshee only affects macOS – PC users are not at risk from this new type of malware. Additionally, this malware relies on user input. More cautious or suspicious users are therefore less likely to be threatened by this new stealer. In particular, macOS users with low security awareness are at risk from Banshee.
Banshee and Stealerware
- Stealerware refers to a specific type of malware designed to extract data from an infected device and send it to its creators.
- Banshee is a recently discovered stealerware that exclusively targets Macs.
- The infection of a device does not exploit known vulnerabilities in Macs but relies solely on human factors.
- Banshee collects Safari cookies, accesses the Notes app database, gathers data from browser extensions in other browsers, and targets crypto wallets.
How Does Banshee Spread and Do Antivirus Programs Protect?
The discovery of Banshee is still relatively new, so it is not yet clear how the spread occurs. However, it is suspected that Banshee spreads “traditionally” through phishing links on scam sites. Unfortunately, there are no warnings from common antivirus programs about Banshee yet – the best protection at this point seems to be carefully considering when and where to enter your system password.
Protecting Against Account Compromise Through Leaked Credentials
The discovery of Banshee highlights the importance of protecting against the risks posed by stolen credentials. Even if companies comprehensively secure their security infrastructure, the risk remains that employee and customer accounts are compromised due to reused or password manager-stored passwords. This is where Identeco comes into play.
Identeco collects leaked credentials from various sources on the internet and makes them available to companies to compare with their own user accounts. This allows potentially compromised accounts to be identified and secured before criminals can exploit them. This complements the security measures implemented on the company’s platform and provides an additional layer of protection without violating data protection requirements.
Private users can use the free Leakchecker from the University of Bonn to check their personal risk from stolen credentials published in the Deep and Dark Web. Identified credentials and accounts should be secured immediately. Passwords that have been published should be changed everywhere and no longer used in the future.
Conclusion
Stealerware is a dangerous type of malware that silently steals sensitive data from infected devices and transmits it to the attackers. Unlike ransomware, stealerware often remains undetected for a long time, making data theft particularly effective.
The Banshee Stealer is a new example of this malware, targeting macOS specifically. Banshee does not exploit macOS security vulnerabilities but gains access through the user’s input of the system password. As a result, macOS users with low security awareness are particularly vulnerable to Banshee.
To protect against Banshee, users should be especially vigilant when entering their system password, particularly on unknown or suspicious websites or in unclear prompts during seemingly regular operations. It is recommended to enhance security awareness, regularly apply security updates, and, if necessary, use specialized anti-malware tools. Identeco allows companies to automate the checking of their employees’ and customers’ credentials for threats from leaked data and even proactively protect against them. Private users are advised to regularly analyze their risk using the Leakchecker from the University of Bonn to quickly identify threats and secure affected accounts.
Artikel teilen