Phishing #1: Email Phishing, Baiting and Search Engine Phishing
- Reading time:
- 3 min

The number of phishing attacks increased by 29% in 2021 compared to the previous year, and Germany was the third most attacked country. But what exactly is “phishing”? In phishing, someone poses as a reputable and trustworthy person or company and, by manipulating the victim, achieves that the latter clicks on or opens a file, link or similar. This usually then leads to personal information being stolen or malware being installed.
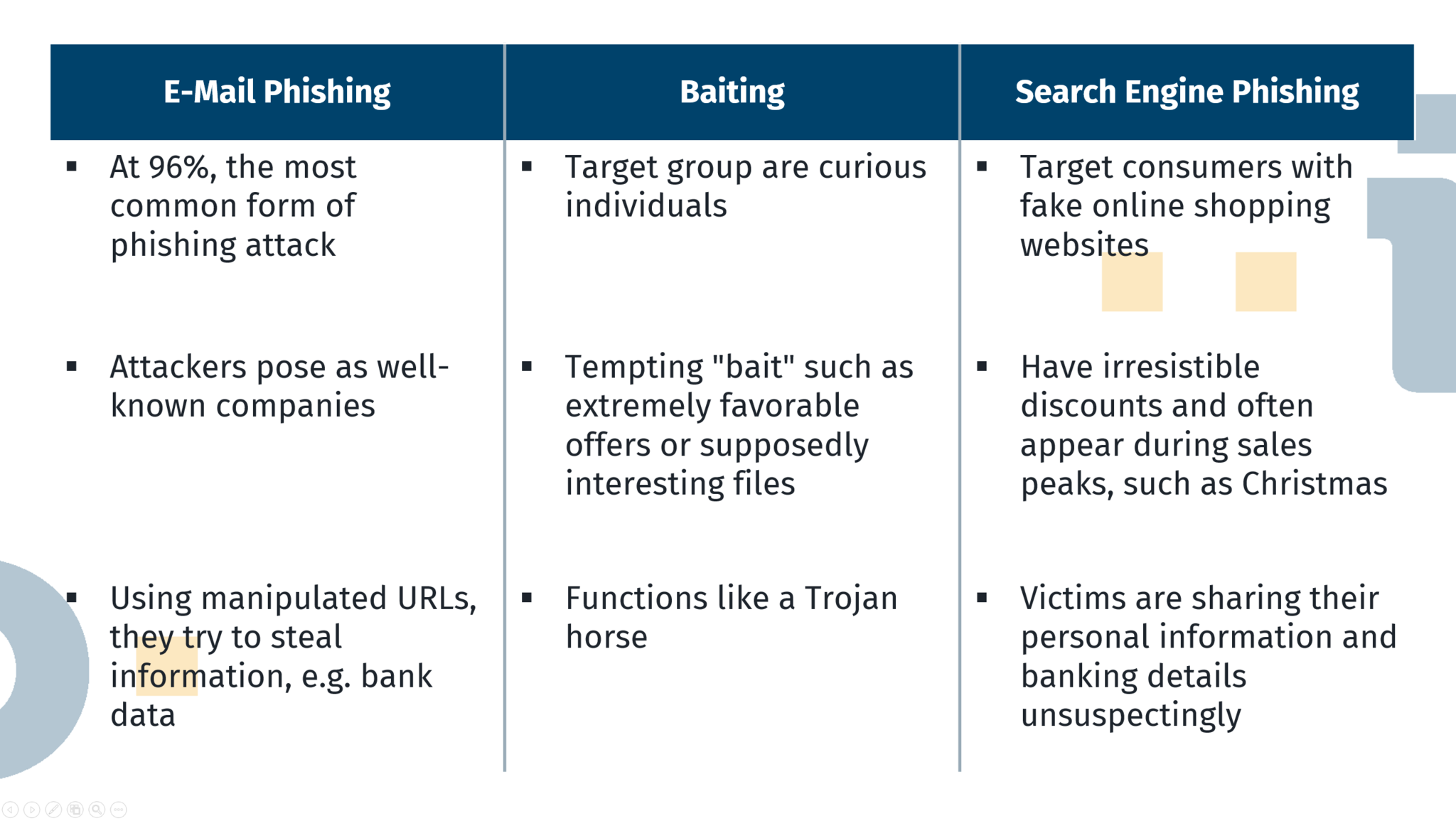
Email Phishing
A well-known example is “email phishing”. This type of phishing accounts for about 96% of all such attacks. Emails are sent that appear to come from well-known companies. Recognizing such e-mails is usually easy and successful if you check the following characteristics in particular:
- Characters are appended to the name of the company, e.g. a dot or an underscore.
- If you look at the sender’s address, they are often random characters.
- The content of the e-mail does not correspond to classic corporate communication. For example, it consists of a short text, which often contains grammatical and spelling mistakes.
Baiting
Besides email phishing, there is also “Baiting”. Baiting is a kind of Trojan horse, which means that while you are interacting with the bait, something is happening in the background, such as downloading malware. Baits are usually interesting file names or even offers. This type of attacks targets curious individuals who, at best, are not familiar with the dangers of phishing. To avoid “Baiting”, one should always make sure that the domain one is on is safe and question the characteristics of the file or offer. One should ask oneself questions like:
- Does the size of the file seem appropriate for what it is?
- Is the file too large?
- Is the offer realistic?
Search Engine Phishing
As you can tell, phishing is everywhere, which means it’s also in your own browser. “Search Engine Phishing” involves targeting consumers with fake online shopping websites. These shopping websites often appear to coincide with the season, e.g. Christmas, and offer irresistible discounts. One unsuspectingly provides personal information and bank details during the purchase and, in most cases, receives nothing of the purchased goods or a cheaper version. Such fake stores can be recognized quite reliably by some features:
- When you are on a shopping website, you can often tell if it is legitimate just by looking at the URL, for example, the name.
- If you are unsure despite the URL, you can briefly research the company. Bad reviews or reports from people who have already been harmed can usually be found with a simple search.
- Here, too, you can ask yourself whether the offers are realistic or whether, for example, the price and scope of the advertised goods differ massively from the offers of established online stores.
Artikel teilen